Introduction
Scaling and catering high-quality video content to a specific audience is the main goal of many professional broadcasters and video content providers. Video streaming CDNs and peer-assisted technologies are business-critical when it comes to optimizing video delivery while maintaining the same level of quality as video files are transported to viewers around the globe.
In this post, we’re going to discuss the ins and outs of Multi CDNs combined with P2P video delivery for video streaming. We will explore what that technology is and how it works, and uncover the benefits of combining a Multi CDN architecture with peer-assisted technologies. To conclude, we share some practical tips on how broadcasters and video content providers can implement these in their own workflows.
What is a Multi CDN strategy?
Before diving into Multi CDN, let’s take a look at CDNs first. A CDN or content delivery network is a collection of Points of Presence (PoPs) or edge servers which are strategically placed across a geographic region with a purpose to accelerate digital media delivery (including video and streaming) to end-users. The main goal of CDNs is to shorten the length that a video has to travel in order to maintain the quality and reduce buffering.
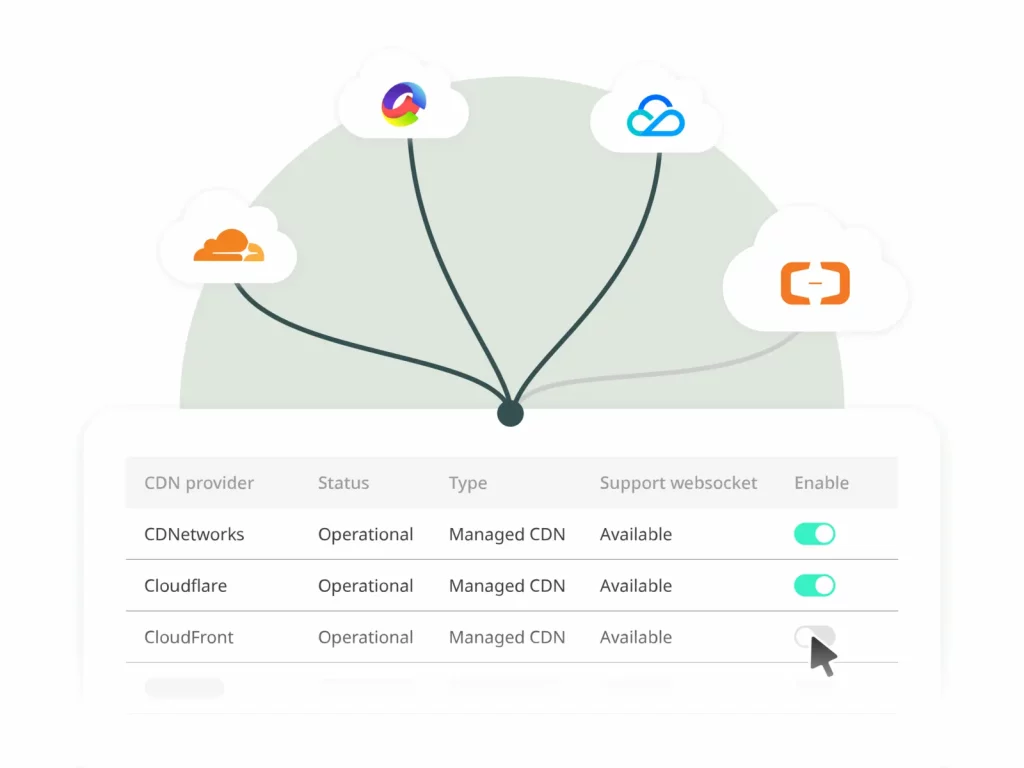
A Multi CDN is a strategy that combines the resources of multiple CDN providers. The resources of each provider are funneled into a single network to make it accessible to content providers like broadcasting professionals.
There is no single CDN that has full global coverage, so combining the infrastructure and resources of different CDN vendors allows you to achieve reliable delivery with a larger global coverage. In addition to coverage, combining multiple CDNs edge servers increases the number of PoPs, directly benefiting delivery performance.
With more coverage, and more PoPs to choose from, your video can reach more locations at greater speed. Additionally, it serves as a backup solution in case that the servers of a particular CDN get congested or experience downtime.